EL(Expression Langugage)
- JSP 2.0 부터 지원
- 데이터를 JSP 페이지 내에 표현하는 기술
- JSP페이지 내의 자바코드를 최소화 하기위해 개발되었다.
- 주로 자바빈과 사용되며, 자바 빈의 프로퍼티 값을 표현식<%= ... %>또는 액션태그<jsp:useBean>을 사용하는 것보다 쉽고 간결하게 꺼낼 수 있게 해준다.
EL의 기본문법 (표현식)
- ${ ... }
- JSP페이지 실행시 즉시 반영된다.
- 객체 프로퍼티 값을 꺼낼때 주로 사용된다.
- #{ ... }
- 시스템에게 필요하다고 판단될 때 사용된다.
- 사용자 입력값을 객체의 프로퍼티에 담는 용도로 주로 사용된다.
예제
- 회원의 정보를 담고있는 Bean이 있고, 서버에서 어떠한 값을 가져온다고 가정하자
public class MemberBean {
private String id;
private String pw;
private String name;
private String birthday;
private String email;
//public MemberBean() {}
public String getId() { return id; }
public void setId(String id) { this.id = id; }
public String getPw() { return pw; }
public void setPw(String pw) { this.pw = pw; }
public String getName() { return name; }
public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; }
public String getBirthday() { return birthday; }
public void setBirthday(String birthday) { this.birthday = birthday; }
public String getEmail() { return email; }
public void setEmail(String email) { this.email = email; }
}
- 서버에서 넘어온 Bean은 어떤 값들을 가지고있을것이고, 배열의형태일수도 있다.
- 그러한 빈의 프로퍼티에 접근하는 el 형태는 총 세가지가 존재한다.
- ${ bean.getter() }
- ${ bean.property }
- ${ bean["property"] }
- 이중 대괄호([])를 사용하는 경우에 가져오고자 하는 property를 큰따옴표 혹은 작은따옴표로 감싸줘야한다.
- 주로 동적인 태그 생성시 JS의 도움을 받을때가 많고, JS는 문자열을 작은따옴표로 감싼다. 때문에 EL의 표현식에서는 큰따옴표를 사용하는것이 편리할때가 많다.
<%@page import="myapp.beans.MemberBean"%>
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%
MemberBean example1 = new MemberBean();
example1.setId("hong1234");
example1.setPw("1234");
example1.setName("honggildong");
example1.setBirthday("20230316");
example1.setEmail("hong@naver.com");
MemberBean example2 = new MemberBean();
example2.setId("gil1234");
MemberBean example3 = new MemberBean();
example3.setId("dong1234");
MemberBean[] arrExample = {example1, example2, example3};
request.setAttribute("example", example1);
request.setAttribute("arrExample", arrExample);
%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>EL</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>EL의 기본 문법</h1>
<h2>${ bean.getProperty() }</h2>
<div>${ example.getId() }</div>
<br>
<h2>${ bean.propery }</h2>
<div>${ example.id }</div>
<br>
<h2>${ bean["propery"] }</h2>
<div>${ example['id'] }</div>
<div>${ example["id"] }</div>
<br>
<h1>Array</h1>
<div>${ arrExample[0].getId() }</div>
<div>${ arrExample[1].id }</div>
<div>${ arrExample[2]['id'] }</div>
<div>${ arrExample[2]["id"] }</div>
</body>
</html>결과

EL의 내장(기본) 객체
- EL또한 JSP의 내장객체처럼 JSP페이지에서 필수적으로 필요한 객체들을 제공해준다.
- 총 11가지가 존재한다.
| 내장 객체 | 설명 |
| pageContext | pageContext 객체를 참조할 때 사용 |
| pageScope | page 영역에 존재하는 객체를 참조할 때 사용 |
| requestScope | request 영역에 존재하는 객체를 참조할 때 사용 |
| sessionScope | session 영역에 존재하는 객체를 참조할 때 사용 |
| applicationScope | application 영역에 존재하는 객체를 참조할 때 사용 |
| cookie | 쿠키 객체를 참조할 때 사용 |
| param | 파라미터 값을 얻어올 때 사용 |
| paramValues | 파라미터 값을 배열로 얻어올 때 사용 |
| initParam | 컨텍스트의 초기화 파라미터를 의미 |
| header | Header 정보를 얻어올 때 사용 |
| headerValues | Header 정보를 배열로 얻어올 때 사용 |
웹 어플리케이션의 저장소
- page, request, session, application의 scope(저장소)를 갖으며, 우측으로 갈수록 사용범위가 넓어진다.
EL에서 보관소 검색 범위 지정
- 사용하는 영역이 엄격하게 구분된다는 점이 JSP의 내장객체와의 가장 큰 차별점이다.
- pageScope, requestScope, sessionScope, applicationScole가 이에 해당되며, Scope가 붙은 내장객체는 기본적으로 생략이 가능했기에 이전 예제인 EL의 기본문법 ${ ... }을 사용할 때 생략하여 사용할 수 있었던 것이다.
- EL의 표현식에서 객체의 Scope를 생략하면 모든 보관소를 검색한다.
| 내장 객체 | 보관소 |
| pageScope | JspContext |
| requestScope | ServletRequest |
| sessionScope | HttpSession |
| applicationScope | ServletContext |
- 보관소를 검색하는 순서는 JspConect -> ServletRequest -> HttpSession -> ServletContext 즉 적은범위부터 찾아나가며, 내장 객체를 통해 검색범위를 지정할 수 있다. 만약 유효 범위(scope)내에서 객체를 찾지 못하였을 경우에는 null을 반환한다.
예제
- 각 scope에 값을 저장한다.
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>El의 Scope</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>EL의 유효 범위(scope)</h1>
<%
pageContext.setAttribute("page", "pageScope");
request.setAttribute("request", "requestScope");
session.setAttribute("session", "sessionScope");
application.setAttribute("application", "applicationScope");
%>
<jsp:forward page="scope2.jsp"></jsp:forward>
</body>
</html>
- 각 scope에 저장된 값을 EL 표현식을 사용해 출력해본다.
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>EL Scope2</title>
</head>
<body>
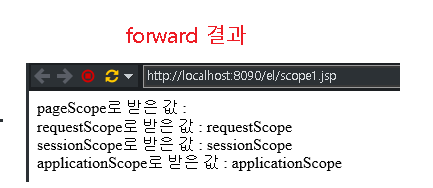
<div>pageScope로 받은 값 : ${ pageScope.page }</div>
<div>requestScope로 받은 값 : ${ requestScope.request }</div>
<div>sessionScope로 받은 값 : ${ sessionScope.session }</div>
<div>applicationScope로 받은 값 : ${ applicationScope.application }</div>
</body>
</html>결과
- forward와, redirect를 통해 페이지를 이동한 결과를 통해 유효 범위(scope) 이해해보자
- pageScope는 forward와 redirect와 상관없이, pageContext로인해 저장소에 저장된 페이지에서만 범위가 유효하다.
- sessionScope와 applicationScope는 페이지의 위치와 상관없이 동일 세션이거나, 어플리케이션인경우 유효하기 때문에 어떠한 방식으로 페이지에 접근하던지간에 유효하다.
- requestScope일 경우에는 forward와 redirect에서 차이가 발생한다.
- forward : 서버측에서 사용자의 요청그대로 새로운 페이지에 요청을 보내기 때문에 request객체가 소멸되지 않고 유지된다.
- redirect : 클라이언트측에서 서버측으로 새로운 요청을 보내기 때문에 request객체가 소멸된다.
- 이러한 차이가 발생하는 이유는 JSP/Servlet Container의 동작방식과 forward와 redirect의 차이점을 생각해보면 간단하다. 클라이언트측에서 서버로 요청을 보내면 Container는 HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse 객체를 새로 생성해 스레드에 할당된 서블릿(JSP)에게 할당한다. 서버가 클라이언트에게 응답을 한 이후에는 이 두 객체를 소멸시키기 때문이다.

https://tatsu.tistory.com/entry/JSPForward%EC%99%80-Redirect%EC%9D%98-%EC%B0%A8%EC%9D%B4
[JSP]Forward와 Redirect의 차이
Forward와 Redirect Forward와 Redirect는 작업 중이 페이지가 전환된다는 점에서 비슷한 역할을 하지만, 이 둘 사이에는 페이지를 전환하는 주체가 다르다는 큰 차이점이 존재하며, 이로인해 동작에 큰
tatsu.tistory.com
https://tatsu.tistory.com/entry/JSP-Servlet%EA%B3%BC-Container%EC%9D%98-%EA%B0%9C%EB%85%90
[JSP] Servlet과 Container의 개념
Applet Client Side 동작방식을 갖는다. 자바로 개발한 응용 프로그램을 웹 페이지와 함께 사용자측으로 보낼 수 있도록 만든 프로그램 클라이언트(브라우저)에서 호출시 클래스 파일이 클라이언트 P
tatsu.tistory.com
Param과 ParamValues
- 웹브라우저 form에서 입력 받은 값을 표현하기 위해 단일 데이터와 복수 데이터(배열)을 처리하는 방법을 제공한다.
- initParam은 web.xml에 설정 후 모든 서블릿에서 전역으로 사용할 수 있으나 굳이 다루지는 않았다.
예제
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
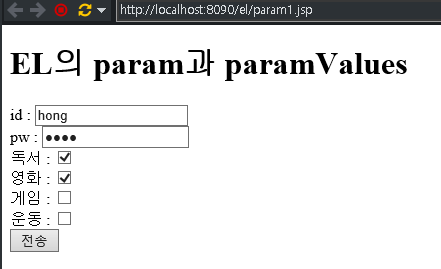
<h1>EL의 param과 paramValues</h1>
<form action="param2.jsp" method="get">
<div>id : <input type="text" name="id"></div>
<div>pw : <input type="password" name="pw"></div>
<div>독서 : <input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="독서"></div>
<div>영화 : <input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="영화"></div>
<div>게임 : <input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="게임"></div>
<div>운동 : <input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="운동"></div>
<input type="submit" value="전송">
</form>
</body>
</html>
- EL의 표현식 ${ ... }의 내장객체은 param과 paramValues를 사용한 예제
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>EL의 param, paramValues 받기</h1>
<div>id : ${ param.id }</div>
<div>pw : ${ param.pw }</div>
<div>취미1 : ${ paramValues.hobby[0] }</div>
<div>취미2 : ${ paramValues.hobby[1] }</div>
<div>취미3 : ${ paramValues.hobby[2] }</div>
<div>취미4 : ${ paramValues.hobby[3] }</div>
</body>
</html>결과

header와 headerValues
- 요청 header의 정보를 얻어올 때 사용한다.
예제
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>EL Header</title>
</head>
<body>
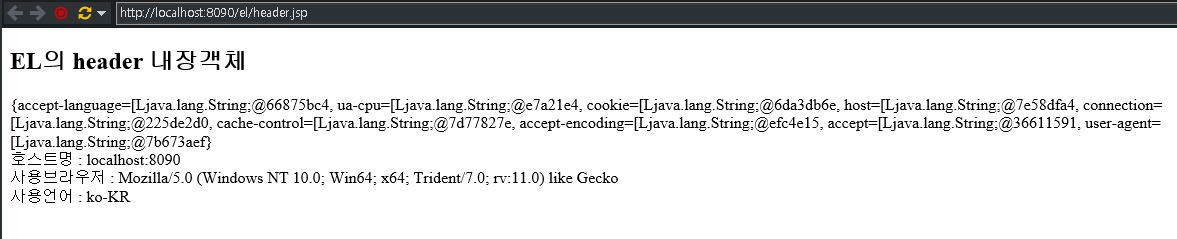
<h2>EL의 header 내장객체</h2>
<div>${ headerValues }</div>
<div>호스트명 : ${header.host}</div>
<div>사용브라우저 : ${header["user-agent"]}</div>
<div>사용언어 : ${header["accept-language"]}</div>
</body>
</html>결과
EL 연산자
- EL의 표현식 내부에서 산술, 논리, 비교, 삼항연산자를 지원한다.
- 기존 연산자와 사용방법이 크게 다르지 않기 때문에 자세히 다루지는 않을것이나,
- gt, lt, ge, le, eq, ne등 추가된 연산자가 존재하나, 한번씩 사용해보면 크게 어렵지 않을것이다.
예제
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>EL Operator</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
pageContext.setAttribute("j", 31);
pageContext.setAttribute("s", 8);
pageContext.setAttribute("p", 22);
%>
<h1>EL Operators</h1>
<div>J=${ j }, S=${ s }, P=${ p }</div>
<h2>산술연산자</h2>
<div>덧셈 : + ${ j + s + p }</div>
<div>뺄셈 : - ${ j - s - p }</div>
<div>곱셈 : * ${ j * s * p }</div>
<div>나눗셈 / : ${ j / s / p }</div>
<div>나눗셈 div : ${ j div s div p }</div>
<div>나머지 % : ${ j % s % p}</div>
<div>나머지 mod : ${ j mod s mod p}</div>
<h2>논리 연산자</h2>
<div>j == s : ${ j == s }</div>
<div>j eq s : ${ j eq s }</div>
<div>j ne s : ${ j ne s }</div>
<h2>비교 연산자</h2>
<div>j > s : ${ j > s }</div>
<div>j gt s : ${ j gt s }</div>
<div>j < s : ${ j < s }</div>
<div>j lt s : ${ j lt s }</div>
<div>j >= s : ${ j >= s }</div>
<div>j ge s : ${ j ge s }</div>
<div>j <= s : ${ j <= s }</div>
<div>j le s : ${ j le s }</div>
<h2>null값 체크</h2>
<div>j == null ${ j == null }</div>
<div>empty j ${ empty j }</div>
</body>
</html>결과

EL의 정적메서드
예제
- EL의 표현식 내부에서 사용될 정적메서드 정의
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
public class ELMethod {
public static String comma(int number) {
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("#, ##0");
return df.format(number);
}
}
- WEB-INF 폴더에 정적메서드에 관한정보를 컨테이너에게 알리기 위해 tld파일 생성 후 맵핑
<taglib xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" version="2.1">
<tlib-version>1.0</tlib-version>
<jsp-version>2.2</jsp-version>
<short-name>JSPTag</short-name>
<function>
<name>comma</name>
<function-class>myapp.el.ELMethod</function-class>
<function-signature>String comma(int)</function-signature>
</function>
</taglib>
- web.xml에 작성한 tld를 등록한다.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd" version="3.1">
<display-name>myapp</display-name>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>index.htm</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.html</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.htm</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.jsp</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
<jsp-config>
<taglib>
<taglib-uri>/Function.tld</taglib-uri>
<taglib-location>/WEB-INF/tlds/Functions.tld</taglib-location>
</taglib>
</jsp-config>
</web-app>
- JSP페이지에서 taglib 지시자를 사용해 해당 페이지에 등록 후 prefix에는 해당 정적메서드를 사용하기위한 트리거와 정적메서드의 정보를 담고있는 tld위치를 알려준다.
- 이후 prefix:methodName() 의형태로 EL의 표현식 내부에서 호출하여 사용이 가능하다.
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@taglib prefix="m" uri="/WEB-INF/tlds/Functions.tld" %>
<%
pageContext.setAttribute("number", 123456789);
%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>EL Static method</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>EL의 정적 메소드</h1>
<div>result : ${m:comma(number)}</div>
</body>
</html>결과
- 표현식에 정적메서드를 사용함으로써 보다 편의성을 제공할 수 있는 방법이 존재한다.
- 하지만 JSTL을 통해 대부분의 문제는 해결할 수 있을뿐만아니라, 서버측에서 처리할지 클라이언트에서 처리할지에 대해 고민을 해봐야 할 것이다.

'JSP' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [JSP/Servlet] RequestDispatcher와 JSP Model2 (0) | 2023.03.16 |
|---|---|
| [JSP] JSTL (0) | 2023.03.16 |
| [WEB] HTTP 프로토콜에서 상태를 지속시키기 위한 방법들 (1) | 2023.03.15 |
| [JSP] Java Beans와 JSP 빈즈태그 (0) | 2023.03.15 |
| [JSP] 내부객체 (0) | 2023.03.15 |



